A Brief History of Robotics in Factories
The first industrial robot, Unimate, was installed on a General Motors assembly line in 1961. Since then, robotics in manufacturing has evolved rapidly, with developments in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robot control systems. Today, robots are capable of adapting in real time, learning from data, and supporting more than just repetitive tasks, they are essential to warehouse work, distribution centres, and complex supply chain operations.
Types of Industrial Robots
Industrial robot types vary in function, structure, and purpose. Some of the most widely used include:
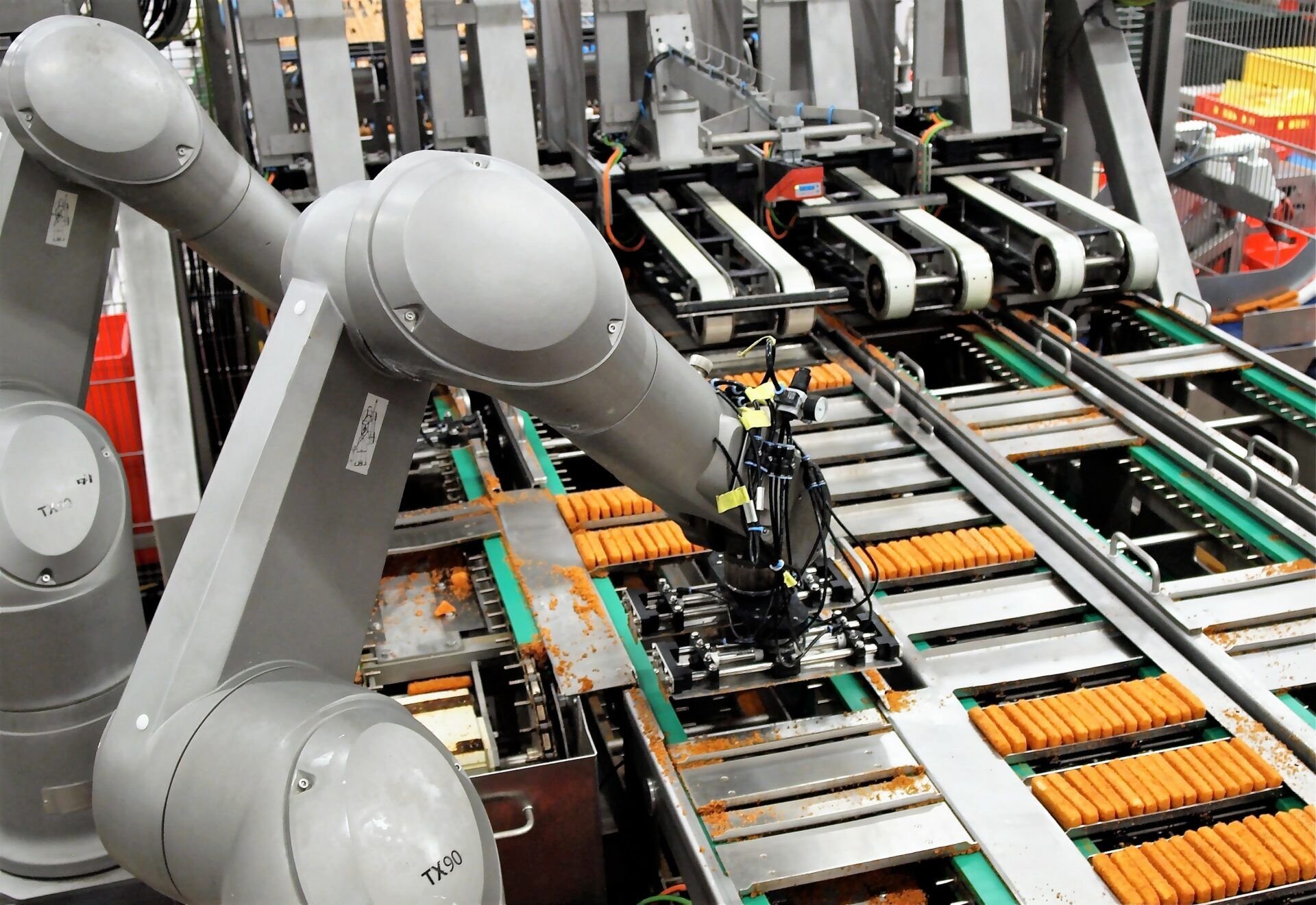
- Articulated robots: These six-axis robots offer a high degree of flexibility, making them suitable for arc welding, Machine Tending, and assembly line automation.
- Delta robots: Known for their speed and precision, delta robots are ideal for pick-and-place tasks in food and electronics packaging.
- SCARA robots: Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arms are commonly used for high-speed assembly and component insertion in electronics manufacturing.
- Cartesian robots: These move in straight lines along the X, Y, and Z axes and are frequently used for tasks like 3D printing or CNC operations.
- Cylindrical robots: Useful in handling applications and tight vertical spaces, cylindrical robots offer a compact solution for certain warehouse layouts.
- Collaborative robots (cobots): Designed to work safely alongside humans, cobots are integrated with vision systems and robot safety features to assist with warehouse productivity.
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs): These autonomous robots navigate distribution centers and warehouses using computer vision and sensor systems to locate, retrieve, and transport goods.
Key Applications of Industrial Robotics
The versatility of industrial robots makes them suitable for a wide range of tasks across industries:
- Palletising and depalletising
- Pick-and-place operations
- Machine Tending in the automotive industry and beyond
- Truck loading and unloading
- Arc welding and metal fabrication
- Conveyor belt system integration for seamless materials movement
- Warehouse automation for e-commerce fulfilment and distribution centres
By integrating robotics with warehouse management systems and warehouse management software, businesses can improve inventory accuracy, reduce manual labour, and increase throughput.