Industrial robots continue to make a dramatic impact on factory operations by taking on a wide range of tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or require high levels of precision. As technology evolves, the scope of these applications continues to grow, helping manufacturers meet increasing demands for speed, consistency, and flexibility.
Here are some of the most common and impactful applications of industrial robots across UK manufacturing:
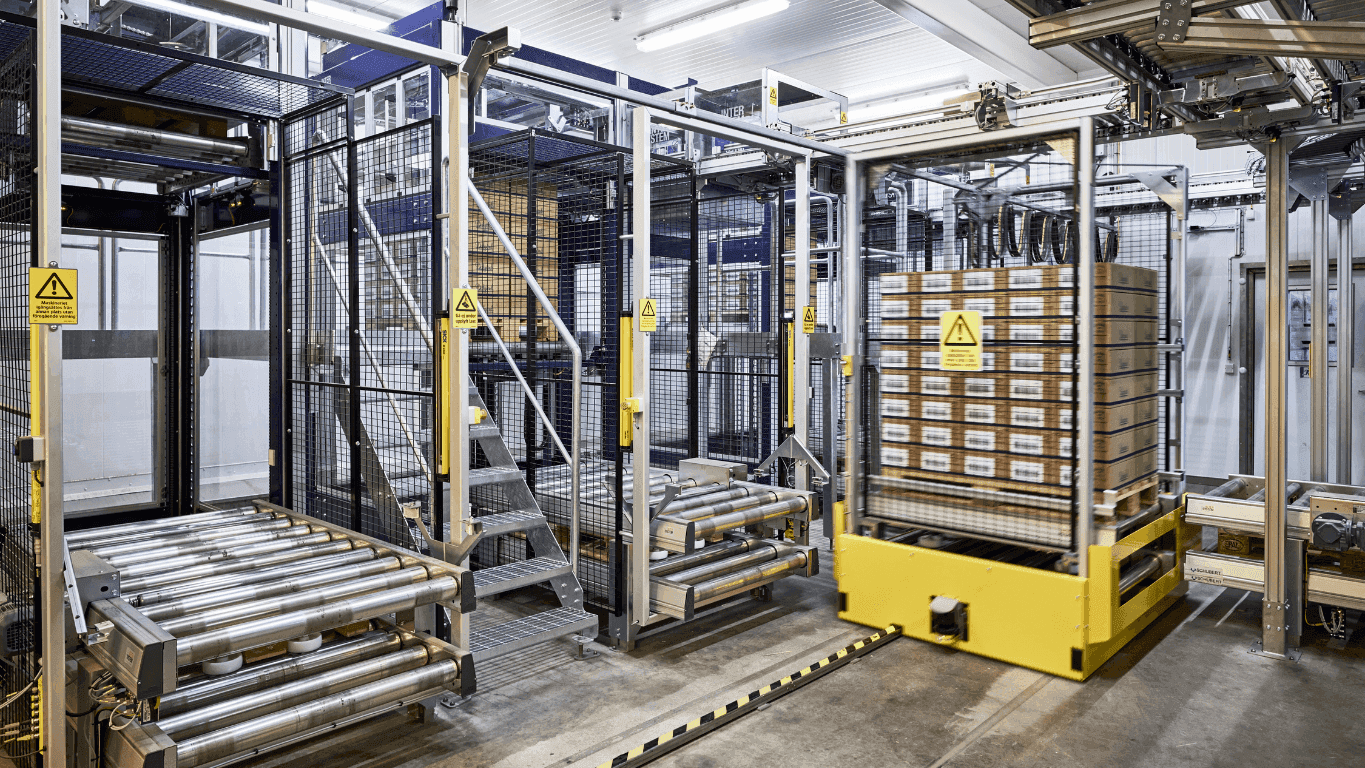
Material Handling
This is one of the most widespread uses of robots in factories. Robots are used to move raw materials, parts, or finished goods between workstations or into storage.
Inspection and Quality Control
Modern robotic arms equipped with advanced machine vision systems can perform multiple inspection tasks.
- Visual Defect Detection: Identifying scratches, dents, or misalignments.
- Dimensional Inspection: Measuring critical features of a part to ensure it meets tolerances.
- Barcode and Label Verification: Ensuring correct product labelling and traceability through product data tracking.
Packaging and Labelling
In the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical sectors, robotic systems manage high-volume, high-speed packing operations while providing compliance with strict hygiene requirements.
- Primary and Secondary Packaging: Handling individual items or grouped packages.
- Label Application: Applying and verifying correct labels based on product type or market.
- Sorting for Distribution: Preparing items for different shipping destinations or retail channels.
Assembly
Robots can perform delicate or repetitive assembly operations with high levels of accuracy and speed.
- Micro-assembly: Especially valuable in electronics, where components are small and complex.
- Fastener Installation: Screwing, riveting, or clipping parts together in consistent cycles.
- Component Fitting: Inserting gears, bearings, or other parts into assemblies using automation control.
Welding
Robotic welding systems are extensively used in the automotive industry, aerospace, and metal fabrication sectors.
- Arc Welding: Ideal for long seams and complex geometries in vehicle body construction.
- Spot Welding: Frequently used on car production lines for joining body panels.
Benefits include higher consistency, stronger welds, and reduced waste. With the integration of vision systems, robots can also adjust to small variances in part orientation or positioning, enabling greater flexibility.
Painting and Coating
Robotic painting is widely used in automotive and appliance manufacturing, where surface quality is critical.
- Ensures uniform coating thickness and finish.
- Reduces overspray and waste of materials.
- Protects workers from inhaling toxic fumes or working in flammable environments. AI-enhanced robots are even capable of real-time decision-making, allowing for adaptive sorting or reworking of defective items through remote operation.
Surface Finishing and Polishing
Robots perform high-precision polishing, sanding, or buffing tasks, especially on parts requiring a flawless surface.
- Widely used in aerospace, automotive, and luxury goods.
- Eliminates human fatigue and variability in results.
This diverse range of applications illustrates why industrial robots have become essential tools across so many sectors. Their ability to adapt to new roles via programming or modular tooling, as well as integration with artificial intelligence and smart manufacturing technologies, allows UK factories to respond quickly to changing market needs and customer specifications to fulfil a wide range of tasks with impressive levels of precision and repeatability.